test for meniscal tears|special test for meniscal tear : importer The McMurray test is a series of movements to check your symptoms and range of motion (how far you can move your knee joint). The test is simple and includes the following steps: 1. You’ll lay on your back. 2. Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it . See more WhatsApp , WhatsApp - WhatsApp
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBBem-vindo à PlayPIX, os melhores jogos e a melhor odd do mundo para sua aposta esportiva estão aqui. Visite o site para saber mais!
The McMurray test is a series of movements to check your symptoms and range of motion (how far you can move your knee joint). The test is simple and includes the following steps: 1. You’ll lay on your back. 2. Your provider will bend your knee to 90 degrees perpendicular to the rest of your body (about where it . See moreYou don’t need to do anything to prepare for a McMurray test. Just visit your provider as soon as possible if you’ve injured your knee or you notice any new . See more
Try to relax while your provider is moving your leg and knee during a McMurray test. Because the McMurray test is a series of physical motions, make sure . See more
A McMurray test is usually a first step in treating your knee. If your provider feels or hears anything in your knee during a McMurray test, they’ll recommend either . See moreThere are no risks to your knee from your provider performing a McMurray test. You might feel a little pain or discomfort during the test, but even if your meniscus . See more
Purpose. McMurray's test is used to determine the presence of a meniscal tear within the knee. Technique. Patient Position: Supine lying with knee completely flexed. Therapist Position: on . The Thessaly test for detection of meniscal tears: validation of a new physical examination technique for primary care medicine. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(1):9-12. Email letter submissions to.
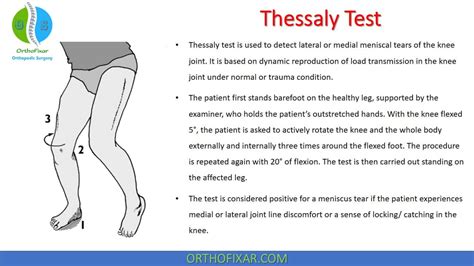
thessaly test for meniscal tear
Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive .

The Apley's grind test (Apley Compression test) is used to evaluate individuals for problems of the meniscus in the knee. This test is named after Alan Graham Appley (1914 - 1996), a .Meniscus tears are among the most common knee injuries. Athletes, particularly those who play contact sports, are at risk for meniscus tears. However, anyone at any age can tear a meniscus. . One of the main tests for meniscus .
If the test is positive (suggesting a meniscal tear), the patient will feel pain and the clinician will feel and/or hear meniscal movement when the meniscus is compressed between the tibia and femur 32. Figure 2. Apley test (grinding) .
Meniscal tears are the most common lesions followed by the meniscal cyst. Both of them have 2 causes. The first one is traumatic and the second one is a degenerative meniscal tear. . Pjotr, et al. "Validity of the Thessaly test in evaluating meniscal tears compared with arthroscopy: a diagnostic accuracy study." journal of orthopaedic .
special test for meniscal tear
Reliability of the Test [edit | edit source]. Many studies have attempted to quantitate the reliability of various physical examination findings. In a prospective study comparing preoperative joint line tenderness to arthroscopic findings of meniscal tears, the sensitivity of joint line tenderness was found to be 86% and 92% with an overall accuracy rate of 74% and 96% for the medial and .
This test won’t show a meniscus tear. However, it can be helpful to determine if there are any other causes of your knee pain, like osteoarthritis. MRI.Medial meniscus: A medial meniscus tear affects the cartilage on the inside of your knee. Lateral meniscus: A lateral meniscus tear affects the cartilage on the outside of your knee. How common are meniscus tears? A torn meniscus is a very common sports injury. Often, athletes and people who play sports for fun get meniscus tears.
With a sensitivity of ~95% and a specificity of 81% for medial meniscal tears and sensitivity of ~85% and a specificity of 93% for lateral meniscal tears 2,5, MRI is the modality of choice when a meniscal tear is suspected, with sagittal images being the most sensitive 5. There are three basic MR characteristics/criteria of meniscal tears 5:Purpose: The McMurray test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus, specifically testing for meniscal tears.Meniscal tears are the most common injury to the knee. The McMurray test is commonly performed along with the joint line tenderness test to identify meniscal injury.
Patients with suspected meniscal tears experience medial or lateral joint-line discomfort and may have a sense of locking or catching. The Thessaly test is a dynamic reproduction of joint loading in the knee and the theory behind the test is that the knee with a meniscal tear will produce the same symptoms the patient reported. A meniscus tear results in pain in the front of the knee, either in the middle of the knee (from a medial meniscus tear, which is more common) or the side of the knee (from a lateral meniscus tear). Often with a torn meniscus, a person can still walk and even continue to play their sport right after the injury.
For lateral meniscus tears, Ege's test gave results superior to the others: 0.84 accuracy, 0.64 sensitivity and 0.90 specificity. Ege’s test is more specific than sensitive. Looking at the different types of Meniscal tears, Akseki et al. found that degenerative tears of the medial menisci were missed in 66% (8 of 12!). Medial meniscal tears .Generally, meniscal root tears are less common than meniscal body tears. The diagnosis of an medial meniscus injury is considered to be fairly certain if three or more of the following findings are present: Tenderness at one point over the medial joint line; Pain in the area of the medial joint line during hyperextension of the knee jointHowever, meniscus tears do not always appear on MRIs. Meniscus tears, indicated by MRI, are classified in three grades. Grades 1 and 2 are not considered serious. They may not even be apparent with an arthroscopic examination. Grade 3 is a true meniscus tear and an arthroscope is close to 100 percent accurate in diagnosing this tear. The meniscus tears due to an acute injury (traumatic meniscal tear) or from being worn down over time (degenerative meniscal tear). . Pain accompanied by a snapping, clicking or popping sound suggests a tear is present in the rear of the medial meniscus. The test is then repeated but with inward rotating. A snapping, clicking or clunking .
positive test for meniscus tear
Posterior horn tears are common and located in the back of the meniscus.; Central tears are on the inner side of the meniscus. This part of the meniscus does not have a blood supply and is, therefore, not responsive to .McMurray test (meniscus cartilage tear): Lateral meniscus tear: With patient supine, fully flex the knee, place forefingers on lateral side of joint line, then with applying valgus stress and internal rotation of leg, extend the knee looking for .

Joint line tenderness: Joint line tenderness is a very non-specific test for a meniscus tear.The area of the meniscus is felt, and a positive test is considered when there is pain in this area. McMurray's test: This test is .Internal rotation tests for tears of the lateral meniscus, while external tests the medial meniscus. As this is performed, the doctor lightly touches, or palpates, the knee. In the event of an injury being present, these palpations will produce a thud or click. 1 Hing W, White S, Reid D, Marshall R. Validity of the McMurray’s Test and . This video shows how to perform the McMurray test, one of the most commonly used clinical assessment tools to assess for meniscal injuries in the knee.This v. It’s like a shock absorber that cushions your bones and knee joint. Any sudden and intense jerking motion on your knee can tear your meniscus. Sports injuries are the most common cause, but traumas like falls and car accidents can also tear your meniscus. The most common symptoms of a torn meniscus include: Feeling or hearing a pop in your knee.
With the use of arthroscopic examination, surgeons can prove and refine clinical tests for joint damage. In the case of the meniscus, a C- or horseshoe-shaped piece of cartilage in the knee, the McMurray test is used most often to diagnose posterior (along the back of the knee joint) meniscal tears. Results of the McMurray can be verified during the arthroscopic exam when . Meniscal injuries of the knee are common. Acute meniscal tears occur most often from twisting injuries; chronic degenerative tears occur in older patients and can occur with minimal twisting or stress. Left untreated, large complex tears can impair smooth motion of the knee, cause joint effusions, and may lead to premature osteoarthritis. By contrast, 2022 evidence notes that an MRI is 93% sensitive and 88% specific for medial meniscus tears and 79% sensitive and 96% specific for lateral meniscus tears. The McMurray test is not .Meniscus tears & repairs Overview Symptoms When to see a doctor Diagnosis Treatment. Both the inside and outside of the knee have a meniscus. The meniscus is a firm, elastic, shock absorber that helps stabilize the knee and is important for normal function of the knee joint. It also provides protection of healthy cartilage in the knee.
cm feuchtigkeitsmessgerät preis
Meniscus tears are the most common injury of the knee. The McMurray's test and Joint line tenderness for diagnosing meniscus tear have been widely tested, but results reported by different authors vary. The wide variations reported have an impact on . Physical therapy for a meniscus tear can help you recover a normal range of motion and strength after knee surgery, or help you avoid surgery altogether. Here are some sample exercises your therapist may recommend. . How the 6 Minute Walk Test Works in Physical Therapy. Parallel Bars in Physical Therapy. 8 Exercises for Cervical Radiculopathy.
A meniscal tear occurs in 2 primary planes, vertical and horizontal. Vertical tears are generally the result of an acute trauma, whereas horizontal tears are typically degenerative in nature. Kopf S, Beaufils P, Hirschmann MT, et al. Management of traumatic meniscus tears: the 2019 ESSKA meniscus consensus.
das beste feuchtigkeitsmessgerät
Resultado da 4 dias atrás · Log in with your Gmail account to forward any new incoming email to your Proton Mail inbox. We’ll remove trackers from these forwarded emails and protect your privacy with our zero-access encryption.
test for meniscal tears|special test for meniscal tear